Automatic deploys with GitLab CI
It's time to take your gitlab ci to the next level. Let Gitlab CI automatically deploy to staging and give you the option to manually deploy to production if all tests pass.
In the first part, I showed you how to run cypress in GitLab CI, now it's time to tell GitLab CI to also deploy to staging if all tests pass and give us an option to manually trigger a production deploy from Slack!
Automated staging deploys
As you might already know, it's time to add a new stage in the .gitlab-ci.yml file, let's call it deploy_staging and also define how the deploy should be done. In my example, I am still using wagon for LocomotiveCMS but you can, of course, use whatever you need for your staging deploy here instead.
deploy_staging:
stage: deploy_staging
script:
- sed -e s/APIKEY/$LOCO_API/g config/deploy-testing.yml > config/deploy.yml
- bundle install -j $(nproc) --path vendor
- bundle exec wagon deploy staging -v
cache:
key: ${CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG}
paths:
- vendor/ruby
The part which triggers the deploy is bundle exec wagon deploy staging -v and will only be executed if all the GitLab CI jobs in the pipeline were successful before that if not specified otherwise. If you push to GitLab now it will run the tests and if they pass successfully it will automatically deploy to staging. For this, to work, you need to update your deploy-testing.yml file and add an appropriate entry to allow wagon to deploy to staging. Also, make sure the staging page has the GitLab user with admin permissions, otherwise the deploy won't work with LocomotiveCMS.
Manual production deploys
All it takes for a job to be set to manual deploy is adding the option when: manual in the .gitlab-ci.yml file. Taking what I have shown you so far, a production deploy could look like this:
deploy_production:
stage: deploy_production
only:
- master
script:
- sed -e s/APIKEY/$LOCO_API/g config/deploy-testing.yml > config/deploy.yml
- bundle install -j $(nproc) --path vendor
- bundle exec wagon deploy production -v
when: manualSince I don't want to deploy anything else but the master branch to production, I encourage you to add the only: mater setting. Once this is done, you will be able to manually trigger a deploy from the gitlab web interface which looks like this.
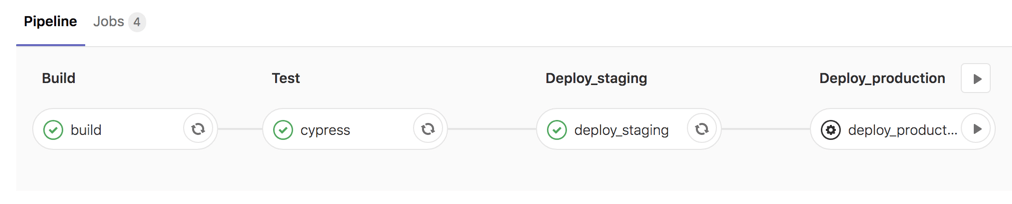
As you can see the staging deploy was done automatically but the production deploy not, as expected and you can click on the "play" icon to trigger the deploy.
Deploying from Slack
Add a Slack Slash command to Gitlab
Let's take this one step further, let's deploy from slack after tests have passed, staging deploy was done and you have checked that the staging deploy looks good. For the Slack deploy to work you first have to add a "Slack Slash command" integration to GitLab. To do this, go to Settings -> Integrations -> Slack Slash Command in Gitlab.
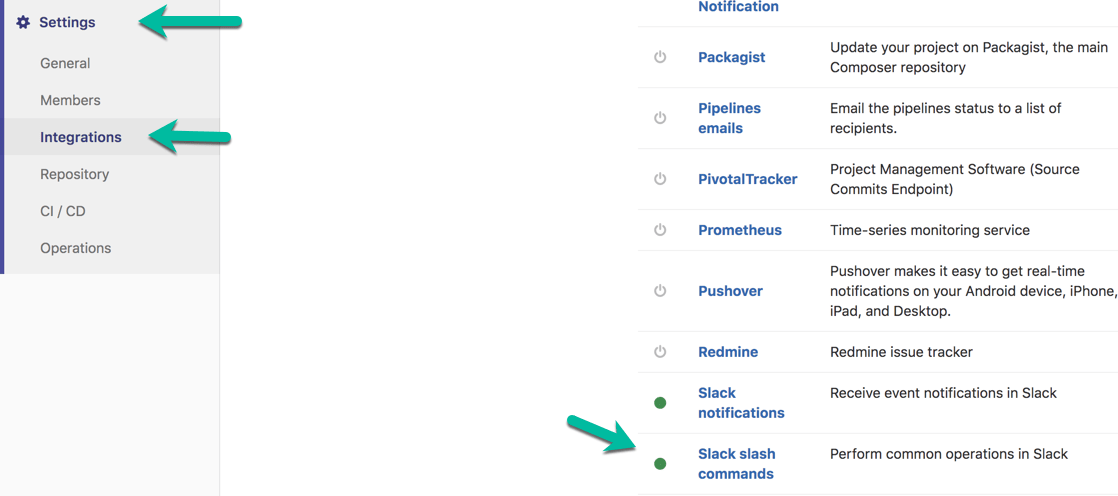
Follow the instructions there and set up the integration, when this is done you need to update your .gitlab-ci.yml
Triggering deploy from Slack
You need to add an environment setting in your gitlab ci config since this is needed for the deploy to work. The slack command to trigger the deploy looks like this: /<command> deploy <env> to <env> hence the environment setting in the gitlab ci config. You should also add a url option to have the URL's for each environment in the Gitlab user interface. Let's take the deploy_staging job and update it with the new settings:
deploy_staging:
stage: deploy_staging
environment:
name: staging
url: https://cms.example.com/locomotive/example-demo/preview
script:
- sed -e s/APIKEY/$LOCO_API/g config/deploy-testing.yml > config/deploy.yml
- bundle install -j $(nproc) --path vendor
- bundle exec wagon deploy staging -v
cache:
key: ${CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG}
paths:
- vendor/rubyand do the same for the production deploy
deploy_production:
stage: deploy_production
environment:
name: production
url: https://www.example.wien/
only:
- master
script:
- sed -e s/APIKEY/$LOCO_API/g config/deploy-testing.yml > config/deploy.yml
- bundle install -j $(nproc) --path vendor
- bundle exec wagon deploy production -v
when: manualIf you now push your code, the tests will run and everything deployed to staging automatically. Since you defined two environments staging and production you can now go in slack and type /app deploy staging to production which will trigger the manual deploy job deploy_production

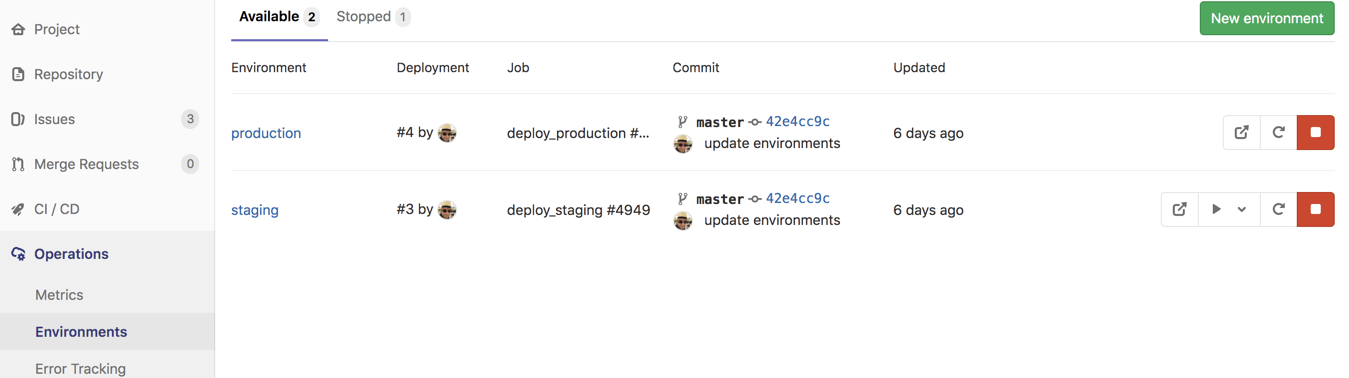
Now why the URL's in the environment definition? Look at your gitlab operations -> environments. Here you will find your two environments with the links to each of the environments as defined in the .gitlab-ci.yml file.
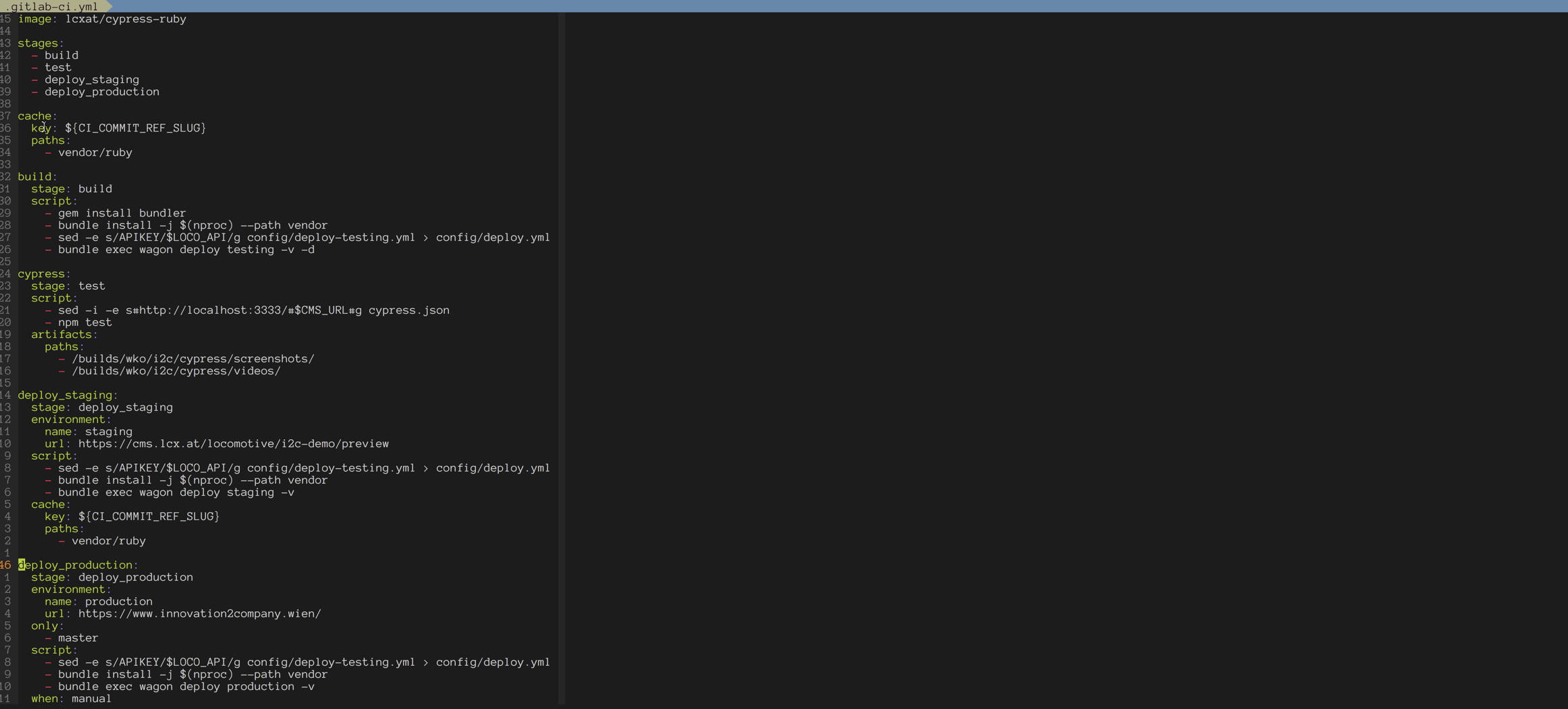
The full gitlab-ci config
Here's the full .gitlab-ci.yml used in this example
image: lcxat/cypress-ruby
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy_staging
- deploy_production
cache:
key: ${CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG}
paths:
- vendor/ruby
build:
stage: build
script:
- gem install bundler
- bundle install -j $(nproc) --path vendor
- sed -e s/APIKEY/$LOCO_API/g config/deploy-testing.yml > config/deploy.yml
- bundle exec wagon deploy testing -v -d
cypress:
stage: test
script:
- sed -i -e s#http://localhost:3333/#$CMS_URL#g cypress.json
- npm test
artifacts:
paths:
- /builds/wko/i2c/cypress/screenshots/
- /builds/wko/i2c/cypress/videos/
deploy_staging:
stage: deploy_staging
environment:
name: staging
url: https://cms.example.com/locomotive/example-demo/preview
script:
- sed -e s/APIKEY/$LOCO_API/g config/deploy-testing.yml > config/deploy.yml
- bundle install -j $(nproc) --path vendor
- bundle exec wagon deploy staging -v
cache:
key: ${CI_COMMIT_REF_SLUG}
paths:
- vendor/ruby
deploy_production:
stage: deploy_production
environment:
name: production
url: https://www.examople.wien/
only:
- master
script:
- sed -e s/APIKEY/$LOCO_API/g config/deploy-testing.yml > config/deploy.yml
- bundle install -j $(nproc) --path vendor
- bundle exec wagon deploy production -v
when: manual